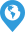
Hey there guys Paul here from the engineering mindset calm in this video we are going to be looking at how heat pumps work now there are a few variants of heat pumps but in this one we're going to be looking at a typical air-source heat pump and these use a reversing valve to allow both heating and cooling modes so first of all the main components you're going to have with any system you'll have an outdoor unit as well as an indoor unit and then a couple of pipes which are insulated just connect them all together now your heat pump system may look slightly differently maybe looks something like this where you've got the carrier outdoor heat pump as well as the your indoor furnace and then that's just ducted after take that and distribute that treated air around the building or home now essentially this system doesn't matter the configuration it all works the same so don't worry too much about that at the moment but let's have a look inside this unit to see the main components and how it works so if we remove the cover we're going to see something like this inside I'll just label up the main components there so you can see what they are so we look at the indoor unit first of all we've got the heat exchanger then we've got the expansion valve in check valve and we've also got a fan inside there then we've obviously got the insulated pipe work which runs and connects to the outdoor unit and in the outdoor unit we've got the compressor which is the driving force of all the refrigerant around the system then we've got the reversing valve there we've also got a heat exchanger on the outside we've also got a lot much larger fan then we've got a check valve and expansion valve there too and then just to show you what how the real components might look like so in the outdoor unit we've got the heat exchanger coil there we've got a check valve will Scout the expansion valve over here but the type of space there.
so we've got a check valve up there and you can see on most of them they'll have a direction of flow arrow on them then we've got the compressor over here that's the scroll compressor in this case and it's a driving force at refrigerant around the entire system and we've got the reversing valve here as the four port reversing valve we're going to look at detail how this works in another video then we've got the outdoor heat exchanger coil and as mentioned we've also got the expansion valve here which is the thermal expansion valve with a capillary tube attached to that now this is just an example of how the real-world components might look and it could be a slightly different setup but this is just to help you understand how the system works so first of all we'll look at how the heat pump works in the cooling mode so as you can see this is just working as a typical air-conditioning unit where we've got the indoor unit acting as the evaporator and the outdoor unit acting as the condenser now the refrigerant is leaving the compressor here and that's leaving us a high pressure high temperature saturated vapor and that heads off straight up into the top of the reversing valve where the reversing valve will decide which which they're actually from floatie and in this case it's being diverted and sent straight to the outdoor heat exchanger where the refrigerant will be condensed and it will give up some of its its energy and you can see these arrows here indicating or showing that there is air being pulled in by this fan the outdoor air which is cooler than the temperature of the refrigerant inside the tubes and some of that energy will be taken away to allow this refrigerant to condense remember that the refrigerant always stays within the tubes it does not leave and the air is not mixed with that now kept completely separately now the temperature of this refrigerant as it leaves the compressor is much higher than the temperature of the air on the outside and that is to allow heat exchange to occur if the refrigerant and the air were the same temperature no heat transfer would occur and the air conditioning system wouldn't work so the greater the temperature difference between the refrigerant and the outside air the greater the heat exchange can so that refrigerant as it enters and passes around it condenses and becomes a liquid so by the time it leaves here and passes through the check valve so when the refrigerant leaves there and passes through this check valve it will be a high pressure up medium temperature saturated liquid and the force of all the refrigerant behind it coming out of this compression compressor is what's pushing that refrigerant all the way around and to the other components in this system so in this configuration the outdoor unit which is acting this condenser is there to reject the heat from the system all the unwanted heat that it will pick up from the indoor unit will be sent to the compressor and that will push it into the condenser where it would get that unwanted heat into the air and push that off into the outside world the fan is just there to help speed up that heat exchange and push that heat out into the world now as that liquid refrigerant is being forced this way up into the indle unit it comes along and hits the check valve and you can see it can only flow in the opposite direction so that will not be allowed to pass through there instead it will head over and pass through the expansion valve instead the expansion valve obviously expands the refrigerant when it leaves the expansion valve
Bergvärme i Stockholm www.xn--bergvrmeistockholm-ptb.se
it will be a low pressure low temperature liquid vapor mixture and this will be pushed around this heat exchanger and that will begin to pick up some of the thermal energy from this wind or the air that's being forced across the coil by this fan so the refrigerant when it enters into the indoor unit which is acting as an evaporator it enters there is a vapor liquid vapor mixture but the refrigerant is a very low boiling point so the temperature of the inside air within the within the building is enough to actually boil this refrigerant and turn it into into a saturated vapor and that's still being pushed out by all the refrigerant that's being pumped behind it from the compressor so by the time it leaves by the time the refrigerant passes through there and leaves the operator or the indoor unit the refrigerant is going to leave as a low pressure low temperature saturated vapor and that's going to head straight back round into the reversing valve which is currently set to divert the refrigerant off straight back into the compressor and that refrigerant will then pass reading a browser and repeat the entire cycle if we now look at how the heat pump would work in a heating mode you can see now the evaporator is actually so the outdoor unit is acting as the evaporator and the indoor unit is acting as the condenser so the refrigerant leaves the compressor again as a high pressure high temperature superheated vapor and this heads straight to the reversing valve where at the moment is being diverted straight towards the indoor unit instead of the outdoor unit the refrigerant enters a condenser and it enters this as a high pressure high temperature superheated vapor and this will give up some of its energy to the air which is blowing across the heat exchanger by the fan this condenses the refrigerant and turns it into a liquid by the time the refrigerant leaves the coil you can see it comes along here and comes towards the check valve an expansion valve and in this instance is going to pass through the check valve because the expansion valve will not let it pass that way so it will flow from here so that refrigerant as is leaving the coil and it's passed through the check valve it will leave there as a high pressure medium temperature saturated liquid and this flows along this liquid line straight down to the outdoor unit you can see here the check valve will not let that pass but it's going to go through the expansion valve instead the expansion valve expands the refrigerant and when that refrigerant passes over the expansion valve is going to leave as a low pressure low temperature liquid vapor mixture it's being pushed through through this coil all the way to the to the other side and it's going to pick up some of the heat from this air that's being blown across it by the fan so that air the outside air which is blowing across the outside heat exchanger that air has enough energy to actually boil the refrigerant again and that's going to turn that refrigerant and after it boils it turn it into a low-pressure low-temperature saturated vapor and that will then head straight towards the compressor where it will then pass through the compressor and repeat the entire cycle again so