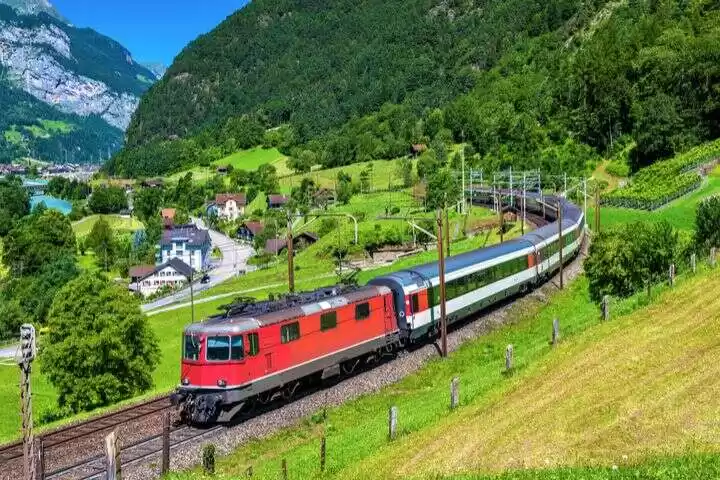
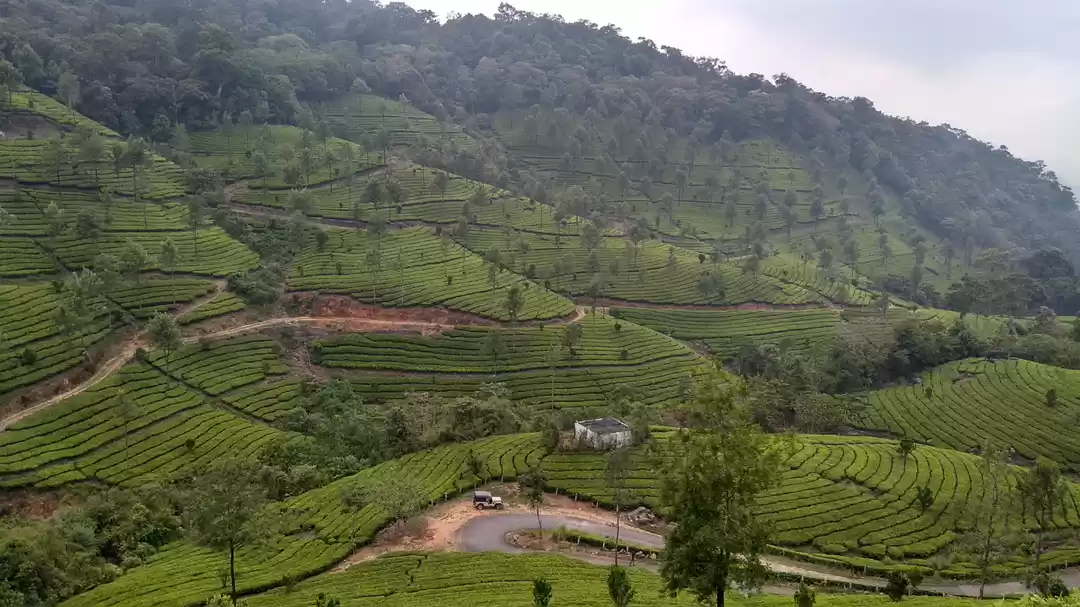
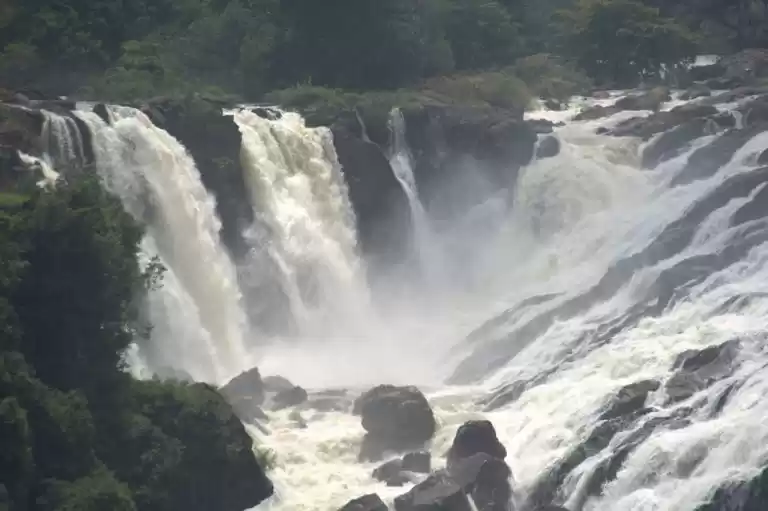
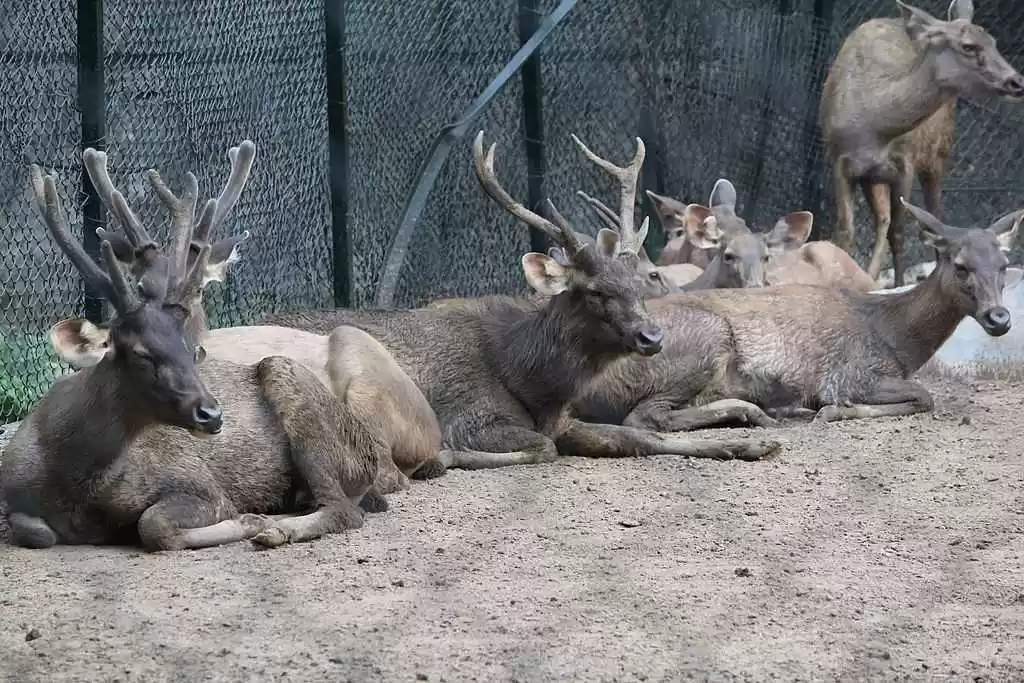
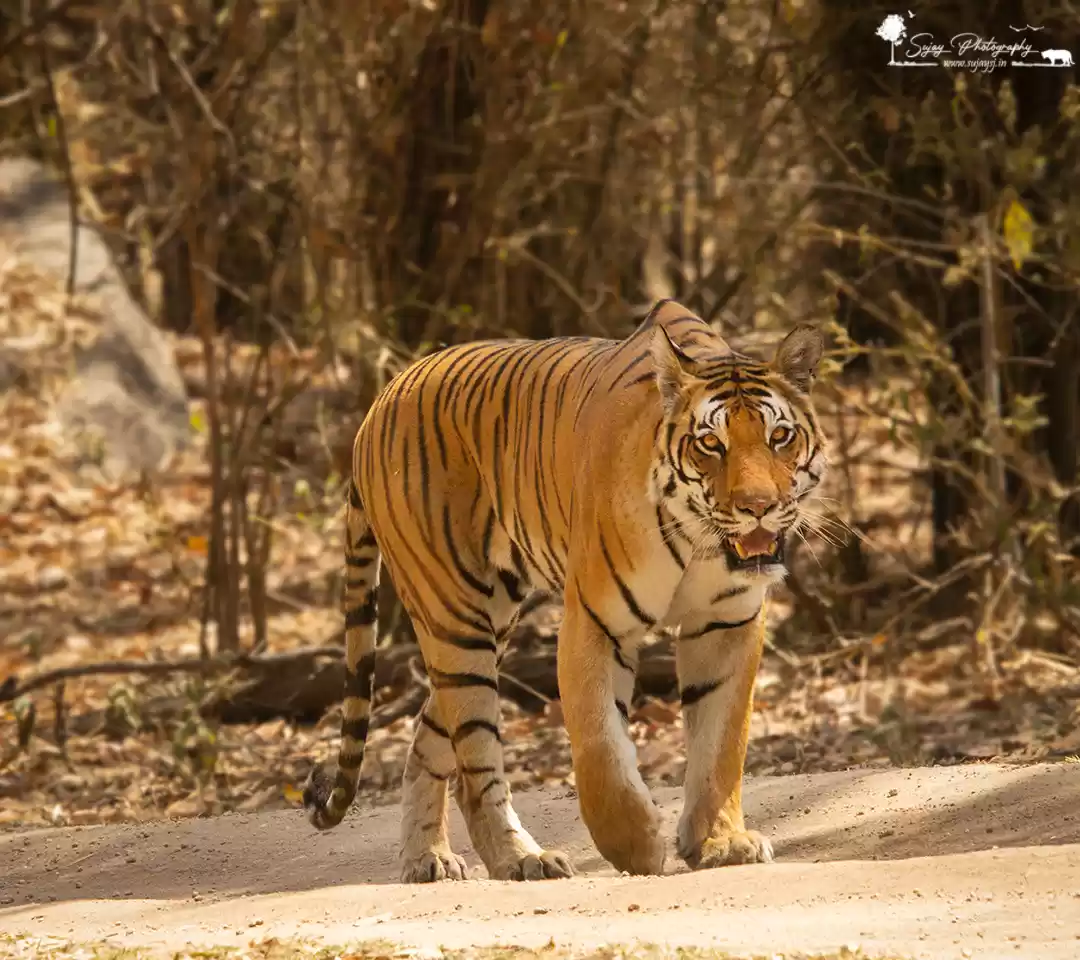
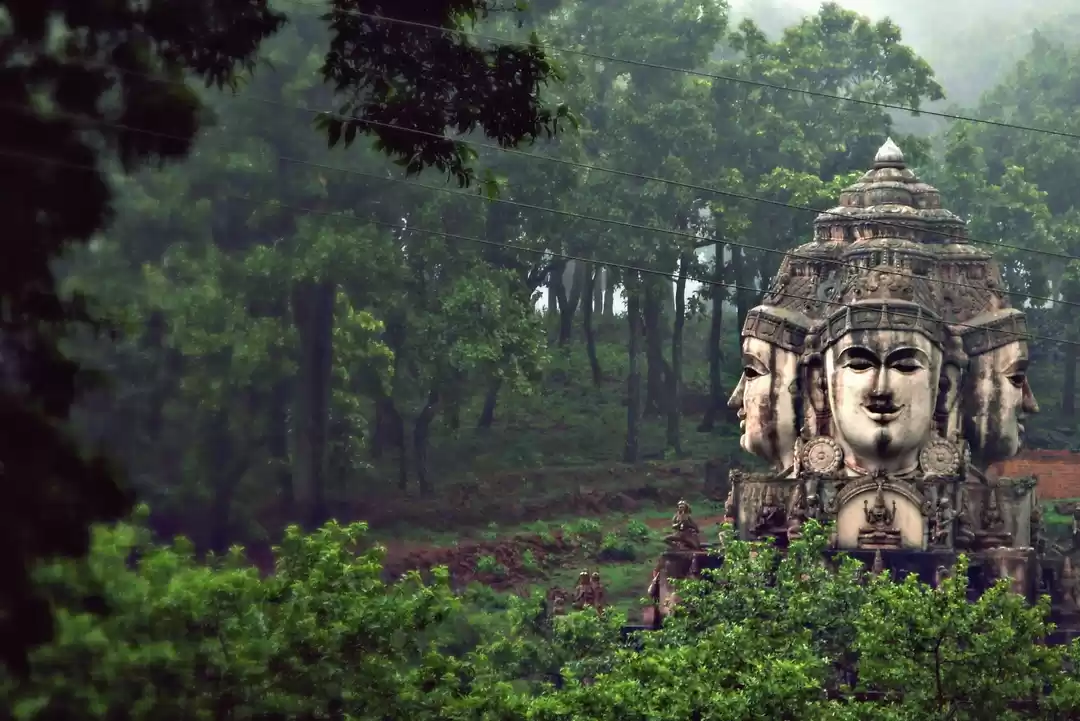
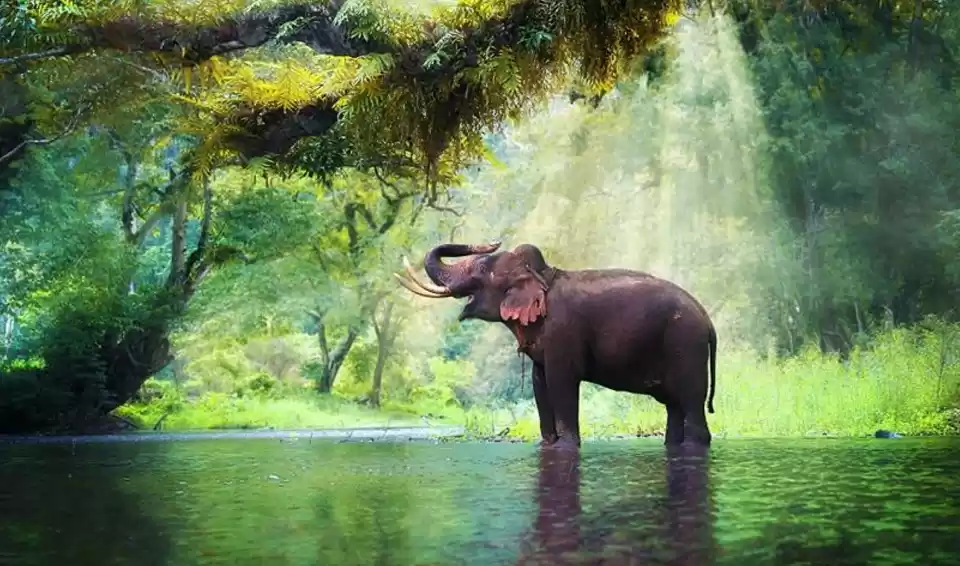
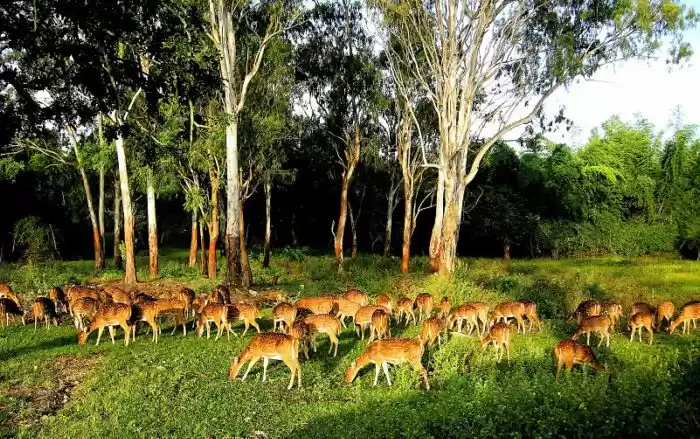
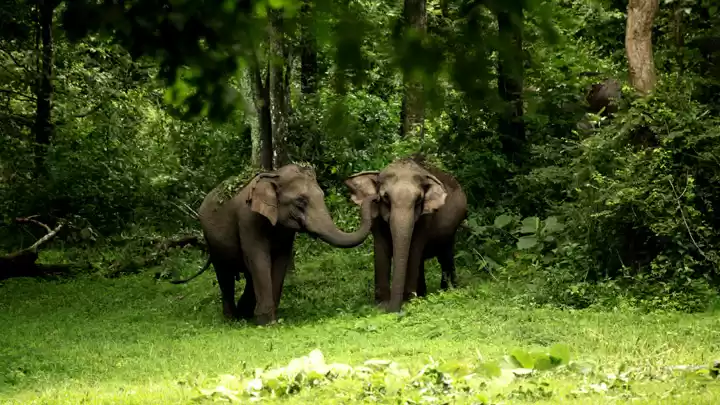
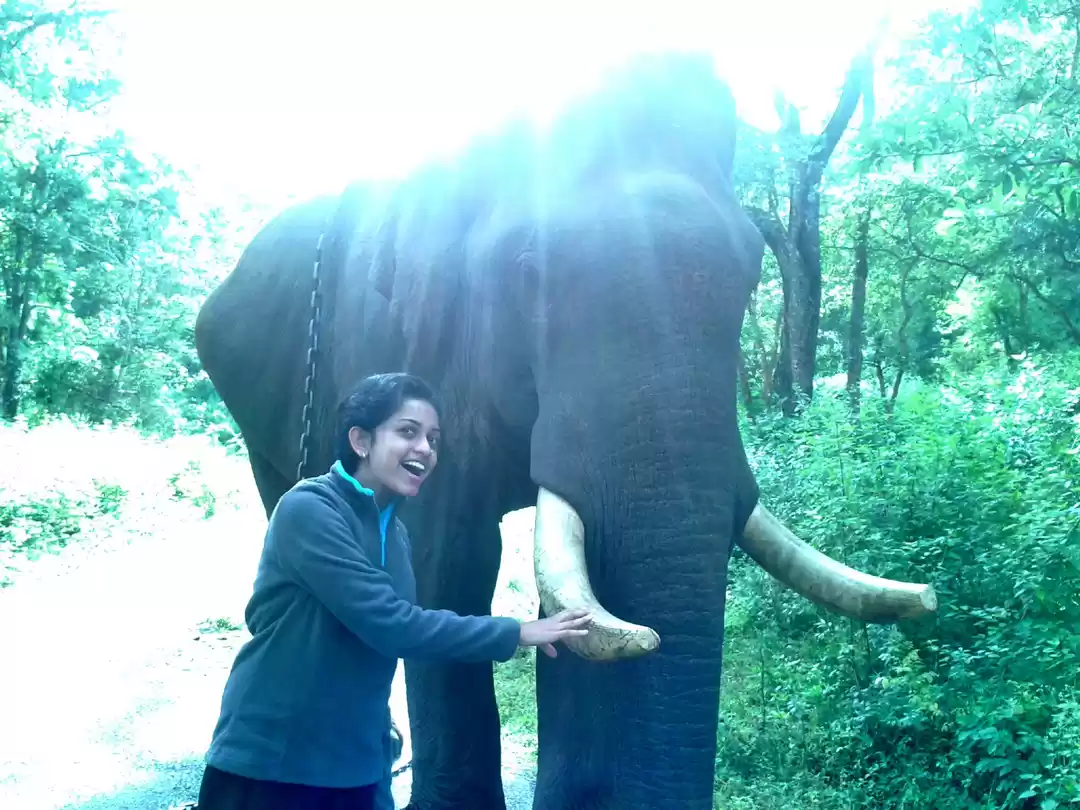
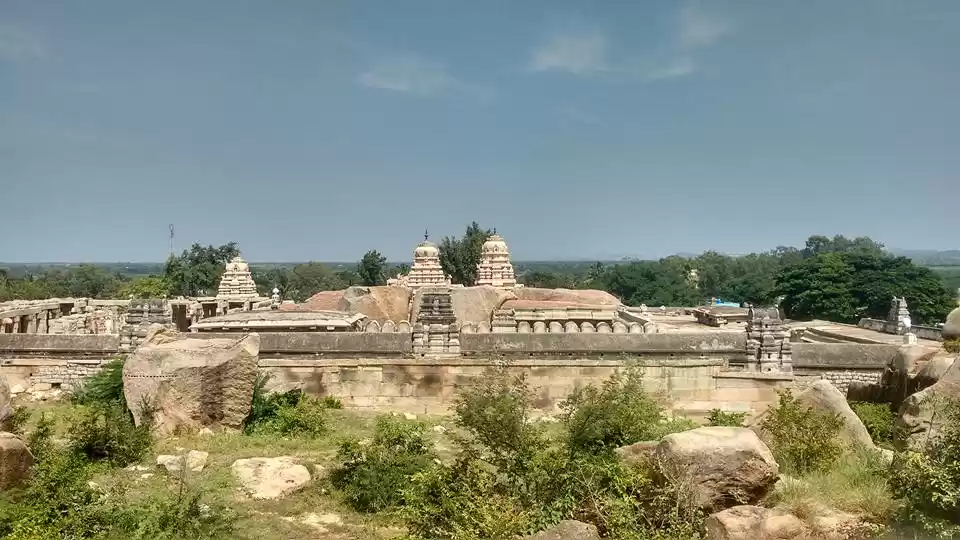
Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve is a protected area and tiger reserve in the Eastern Ghats in the Erode District of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It has a tiger population of 83 individuals and a leopard population of 111 individuals according to the 2019 census.
First various geographical tracts of the Sathyamangalam forests were declared reserve forests. Patches of Sandalwood Reserves were notified under the Indian Forests Act, 1927. The Sathyamangalam Forest Division is part of the Bramhagiri-Nilgiris-Eastern Ghats Elephant Reserve notified in 2003.[1] In 2008, part of the Sathyamangalam Forest Division was declared as a wildlife sanctuary and enlarged in 2011, it covers a forest area of 1,411.6 km2 (545.0 sq mi). In 2013, with an area of 1408.6 sq. km. of the erstwhile sanctuary was notified as Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, the fourth tiger reserve in the state of Tamil Nadu as a part of Project Tiger and is the third largest tiger reserve in Tamil Nadu.
Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve, the Gateway to Eastern Ghats, is a significant ecosystem and a wildlife corridor in the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve between the Western Ghats and the rest of the Eastern Ghats and a genetic link between the five other protected areas which it adjoins, including the Billigiriranga Swamy Temple Wildlife Sanctuary, Sigur Plateau, Mudumalai National Park, Bandipur National Park and the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary. All ranges of the Sathyamangalam and Hasanur Forest Divisions except T.N. Palayam range falls within Sathyamangalam and Thalavadi taluks while T.N. Palayam Range falls both in Sathyamangalam and Gobichettipalayam taluks of Erode District in north western Tamil Nadu
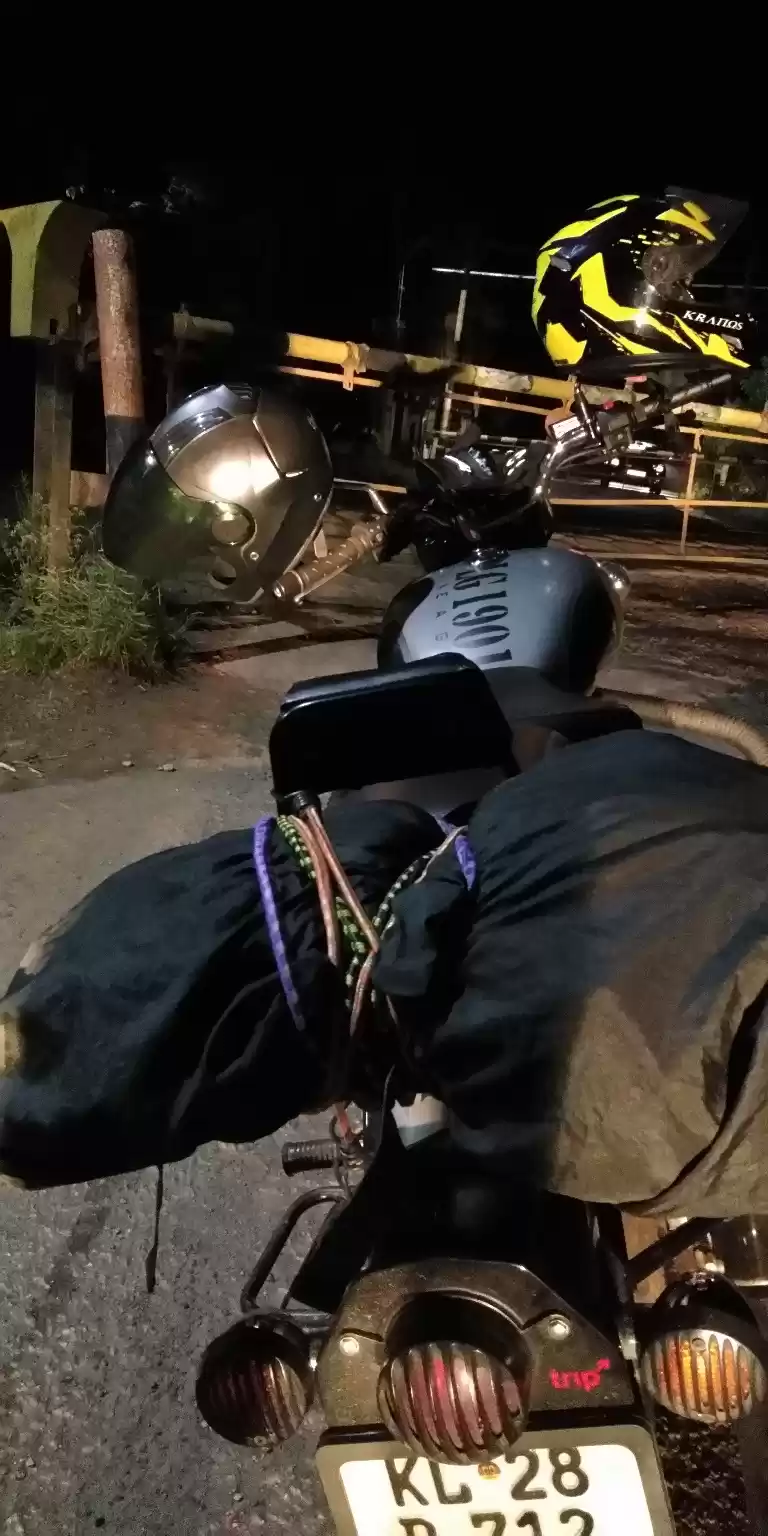
I have travelled across this forest route form my journey from Karnataka's Chamraj Nagar to Palakkad on a bike trip. We came across the forest route to witness a heavy rain which gave us an extra ordinary, tension filled experience.
You can watch the video here.