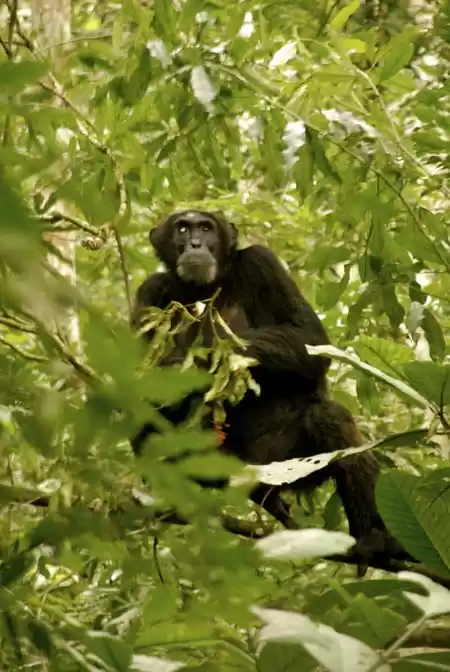
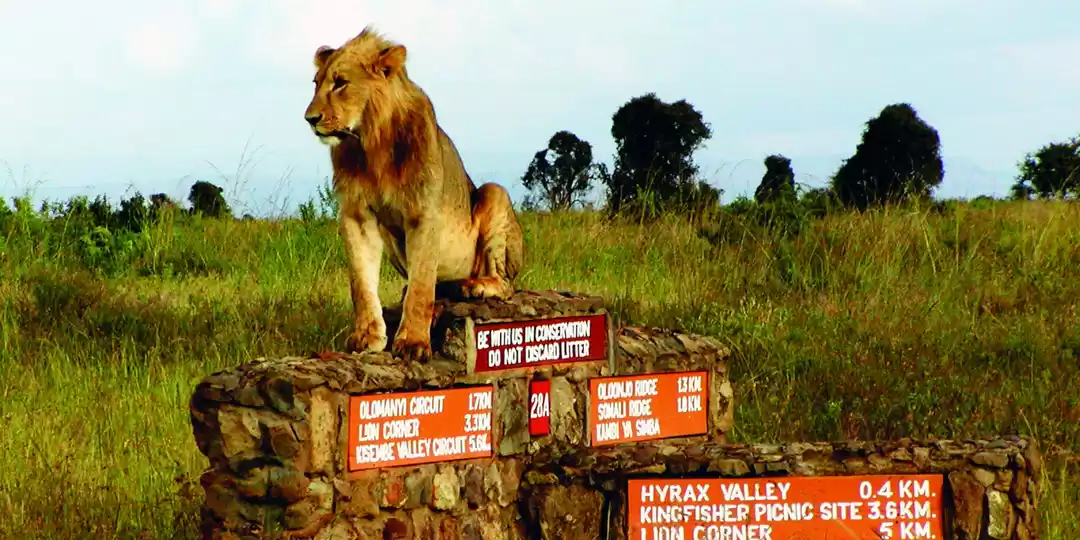
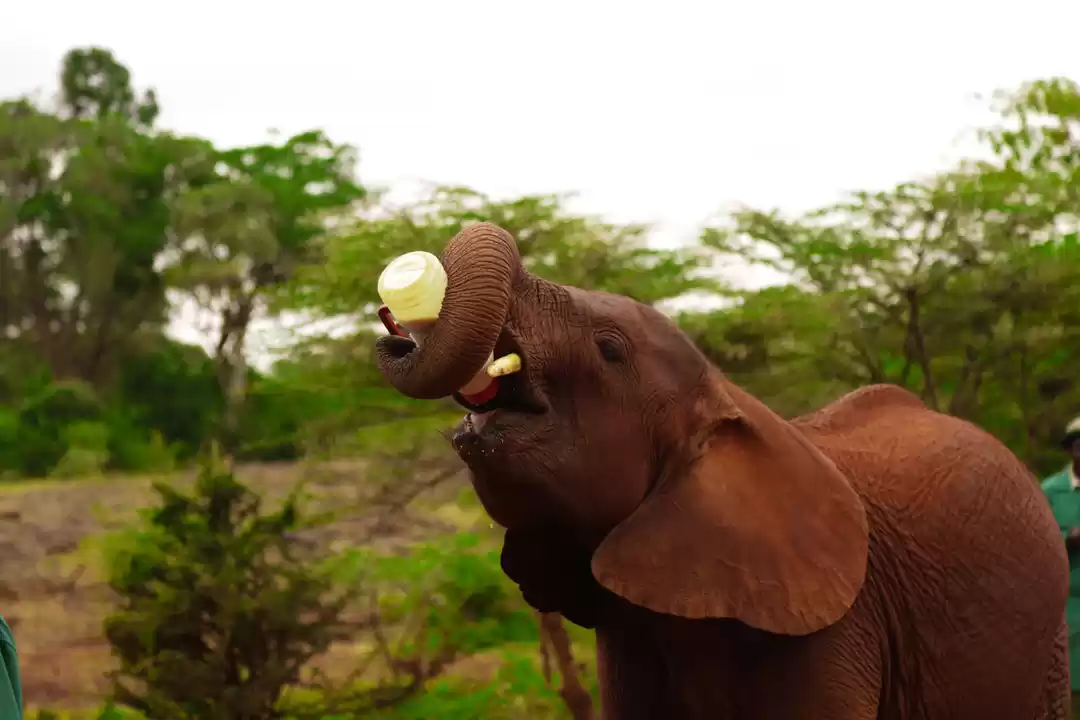
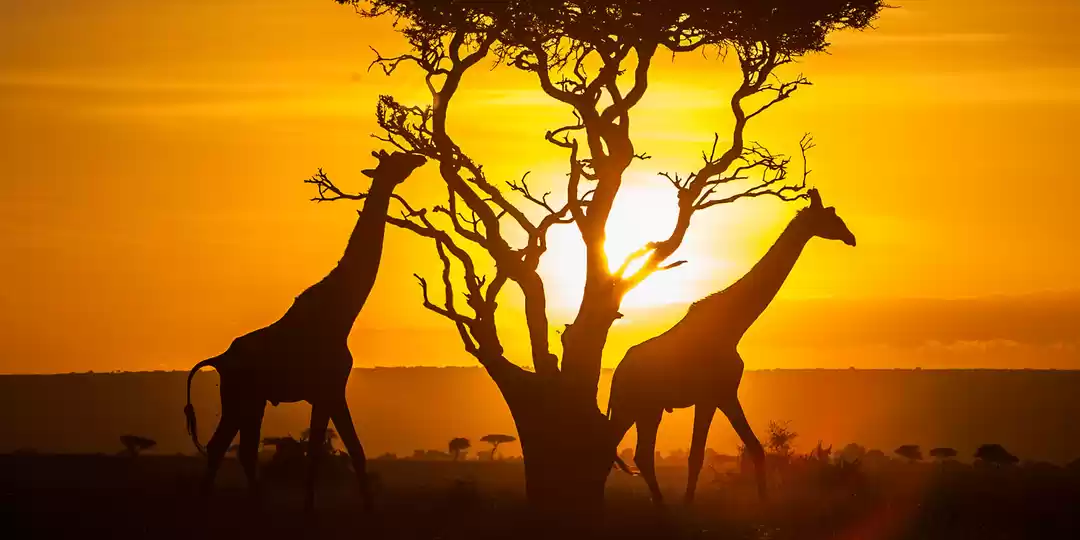
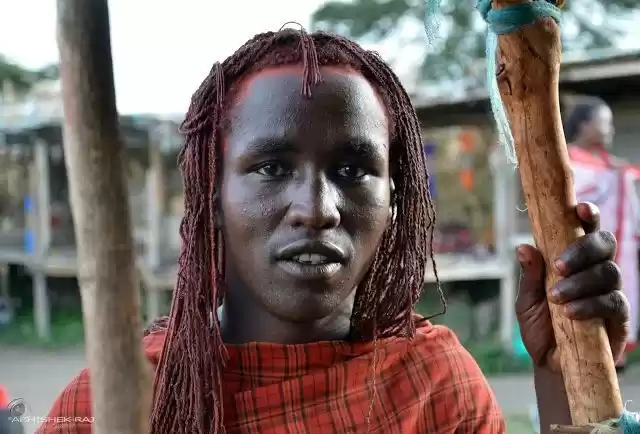
Kenya (/ˈkɛnjə/; locally [ˈkɛɲa]), officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country in Africa and a founding member of the East African Community (EAC). Its capital and largest city is Nairobi. Kenya's territory lies on the equator and overlies the East African Rift covering a diverse and expansive terrain that extends roughly from Lake Victoria to Lake Turkana (formerly called Lake Rudolph) and further south-east to the Indian Ocean. It is bordered by Tanzania to the south, Uganda to the west, South Sudan to the north-west, Ethiopia to the north and Somalia to the north-east. Kenya covers 581,309 km2 (224,445 sq mi), and had a population of approximately 45 million people in July 2014.Kenya has a warm and humid tropical climate on its Indian Ocean coastline. The climate is cooler in the savannah grasslands around the capital city, Nairobi, and especially closer to Mount Kenya, which has snow permanently on its peaks. Further inland, in the Nyanza region, there is a hot and dry climate which becomes humid around Lake Victoria, the largest tropical fresh-water lake in the world. This gives way to temperate and forested hilly areas in the neighboring western region. The north-eastern regions along the border with Somalia and Ethiopia are arid and semi-arid areas with near-desert landscapes. Kenya is known for its safaris, diverse climate and geography, and expansive wildlife reserves and national parks such as the East and West Tsavo National Park, the Maasai Mara, Lake Nakuru National Park, and Aberdares National Park. Kenya has several world heritage sites such as Lamu and numerous beaches, including in Diani, Bamburi and Kilifi, where international yachting competitions are held every year.The African Great Lakes region, which Kenya is a part of, has been inhabited by humans since the Lower Paleolithic period. By the first millennium AD, the Bantu expansion had reached the area from West-Central Africa. The borders of the modern state consequently comprise the crossroads of the Niger-Congo, Nilo-Saharan and Afroasiatic areas of the continent, representing most major ethnolinguistic groups found in Africa. Bantu and Nilotic populations together constitute around 97% of the nation's residents. European and Arab presence in coastal Mombasa dates to the Early Modern period; European exploration of the interior began in the 19th century. The British Empire established the East Africa Protectorate in 1895, which starting in 1920 gave way to the Kenya Colony. Kenya obtained independence in December 1963. Following a referendum in August 2010 and adoption of a new constitution, Kenya is now divided into 47 semi-autonomous counties, governed by elected governors.The capital, Nairobi, is a regional commercial hub. The economy of Kenya is the largest by GDP in East and Central Africa. Agriculture is a major employer; the country traditionally exports tea and coffee and has more recently begun to export fresh flowers to Europe. The service industry is also a major economic driver. Additionally, Kenya is a member of the East African Community trading bloc.The Republic of Kenya is named after Mount Kenya. The origin of the name Kenya is not clear, but perhaps linked to the Kikuyu, Embu and Kamba words Kirinyaga, Kirenyaa and Kiinyaa which mean 'God's resting place' in all three languages. If so, then the British may not so much have mispronounced it ('Keenya'), as misspelled it. Prehistoric volcanic eruptions of Mount Kenya (now extinct) may have resulted in its association with divinity and creation among the indigenous Bantu ethnic groups, who are the native inhabitants of the agricultural land surrounding Mount Kenya.In the 19th century, the German explorer Johann Ludwig Krapf was staying with the Bantu Kamba people when he first spotted the mountain. On asking for the name of the mountain, he was told 'Kĩ-Nyaa' or 'Kĩĩma- Kĩĩnyaa' probably because the pattern of black rock and white snow on its peaks reminded them of the feathers of the cock ostrich. The Agikuyu, who inhabit the slopes of Mt. Kenya, call it Kĩrĩma Kĩrĩnyaga in Kikuyu, which is quite similar to the Kamba name.Ludwig Krapf recorded the name as both Kenia and Kegnia believed by most to be a corruption of the Kamba version. Others say that this was—on the contrary—a very precise notation of a correct African pronunciation /ˈkɛnjə/. An 1882 map drawn by Joseph Thompsons, a Scottish geologist and naturalist, indicated Mt. Kenya as Mt. Kenia, 1862. Controversy over the actual meaning of the word Kenya notwithstanding, it is clear that the mountain's name became widely accepted, pars pro toto, as the name of the country. a b Constitution (2009) Art. 7 [National, official and other languages] '(1) The national language of the Republic is Kiswahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are English and Swahili. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities.' Country Comparison :: Population. The World Factbook. Kenya 2009 Population and housing census highlights at the Wayback Machine (archived 10 August 2013). www.knbs.or.ke. a b c d 'Report for Selected Countries and Subjects (valuation of Kenya GDP)'. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 6 September 2015. a b 'Human Development Report 2014' (PDF). United Nations. 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2014. Ethiopia GDP purchasing power 2010: 86 billion. Imf.org. 14 September 2006. Kenya GDP purchasing power 2010: 66 B llion. Imf.org. 14 September 2006. a b Sullivan, Paul (2006). Kikuyu Districts. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: Mkuki na Nyota Publishers. Krapf, Johann Ludwig (1860). Travels, Researches, and Missionary Labours in Eastern Africa. London: Frank Cass & Co. Ltd. Krapf, Johann Ludwig (13 May 1850). 'Extract from Krapf's diary'. Church Missionary Intelligencer i: 452. Foottit, Claire (2006) [2004]. Kenya. The Brade Travel Guide. Bradt Travel Guides Ltd. ISBN 1-84162-066-1. Ratcliffe, B. J. (January 1943). 'The Spelling of Kenya'. Journal of the Royal African Society 42 (166): 42–44. JSTOR 717465.